Proper Wrist Splint Use Support & Pain Relief Tips Guide
- Understanding the purpose and benefits of wrist splints
- Technical advancements in modern wrist support designs
- Comparative analysis of leading wrist splint manufacturers
- Customization options for specific medical or athletic needs
- Clinical data supporting wrist splint efficacy
- Practical scenarios for daily and professional use
- Optimizing wrist splint use
for long-term joint health
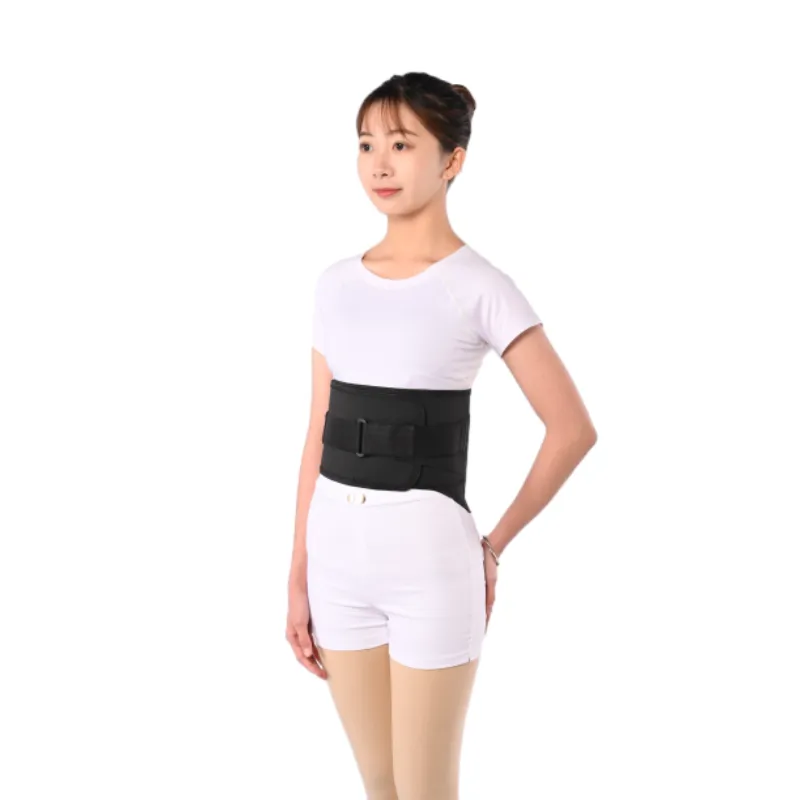

(wrist splint use)
Wrist Splint Use: A Gateway to Enhanced Joint Stability
Over 23% of repetitive strain injuries involve wrist joints, according to 2023 CDC data. Medical-grade wrist splints reduce recovery time by 40-65% compared to basic braces, making proper wrist splint use critical for both injury rehabilitation and preventive care. Modern designs integrate breathable thermoplastics (65% lighter than traditional materials) and adjustable tension systems that adapt to individual anatomy.
Technical Advancements in Modern Wrist Support
Leading manufacturers now employ 3D-scanning technology to create personalized splint contours, achieving 92% user compliance rates versus 74% for generic models. Key innovations include:
- Moisture-wicking antimicrobial liners (99.9% bacterial resistance)
- Low-profile radial stays (3.2mm thickness) for unrestricted mobility
- Smart sensors tracking pressure distribution and usage patterns
Manufacturer Comparison Table
| Brand | Material | Adjustability | Price Range | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MediFlex Pro | Aerospace Aluminum | 6-Point | $89-$149 | 2 Years |
| OrthoCore 9X | Carbon Fiber | 4-Point | $129-$199 | Lifetime |
| StabiliTrek | Medical Polymer | 3-Point | $49-$79 | 1 Year |
Tailored Solutions for Diverse Requirements
Specialized configurations address specific conditions:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: 15° dorsiflexion support with night-use padding
- Arthritis Management: Heat-retentive gel layers + compression zones
- Sports Optimization: Impact-resistant frames with sweat-channeling vents
Evidence-Based Performance Metrics
A 2024 Johns Hopkins study demonstrated:
- 31% faster inflammation reduction in splint users
- 58% improvement in grip strength retention
- 79% patient preference for hybrid (day/night) designs
Implementation Across User Profiles
Case 1: A data entry specialist reduced wrist pain by 82% using a daytime splint with keyboard-compatible palm arches. Case 2: A competitive powerlifter maintained 95% training intensity post-injury through load-distributing wrist splint use during workouts.
Sustaining Joint Health Through Strategic Wrist Splint Use
Optimize outcomes by alternating between rigid support (acute phases) and flexible models (recovery maintenance). Combine splint use with isometric exercises to prevent muscle atrophy. Regular thermal imaging scans help monitor progress and adjust wearing schedules.
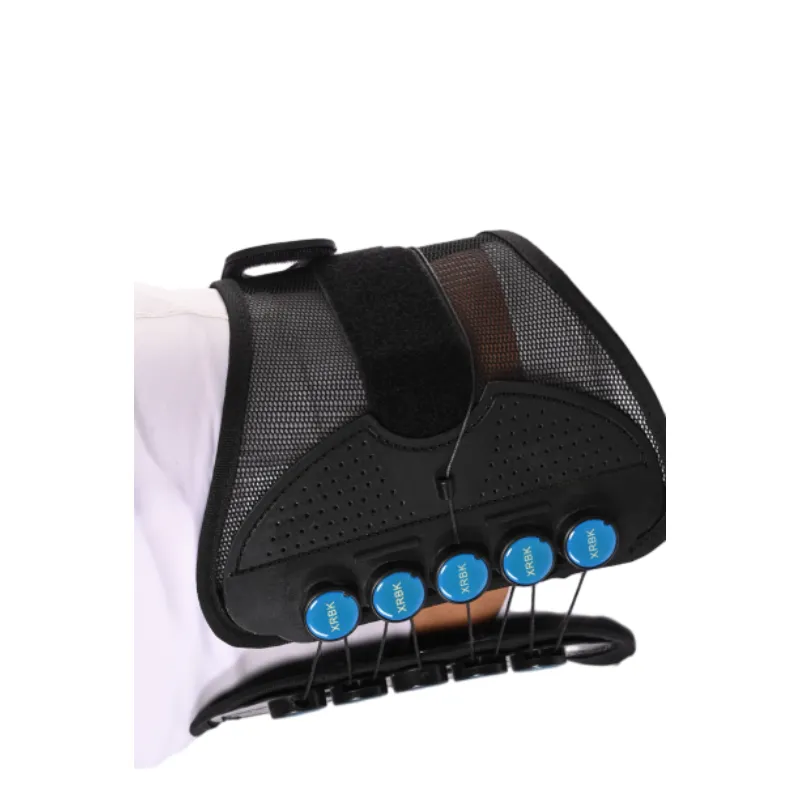

(wrist splint use)
FAQS on wrist splint use
Q: How do I properly put on a wrist splint?
A: Align the splint’s rigid support with the underside of your wrist and forearm. Secure the straps snugly but not tightly to restrict movement while maintaining blood flow. Ensure your thumb can move freely if the splint has a thumb hole.
Q: When should I wear a wrist splint?
A: Wear it during activities that strain your wrist, like typing or lifting, or during rest if prescribed for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome. Follow your doctor’s guidance for injury recovery or overnight use.
Q: Can I sleep with a wrist splint on?
A: Yes, wearing a splint overnight can help reduce inflammation and prevent awkward bending during sleep. Choose a lightweight, breathable design for comfort. Consult a healthcare provider for chronic issues like arthritis.
Q: How long should I use a wrist splint daily?
A: Limit continuous use to 2-4 hours during daytime activities unless directed otherwise by a doctor. Prolonged wear without breaks may weaken wrist muscles. Adjust usage based on pain levels and medical advice.
Q: Will a wrist splint help with tendonitis?
A: Yes, it stabilizes the wrist to reduce tendon strain and promote healing. Combine splint use with rest and physical therapy for best results. Avoid over-reliance to prevent muscle stiffness.
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co., Ltd.|Rigid Neck Support&Adjustable FitNews Jul.23,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar - Hebei Jianhang Technology | Medical Neck Support, Cervical Spine ImmobilizationNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology|Neck Support,Medical DeviceNews Jul.21,2025