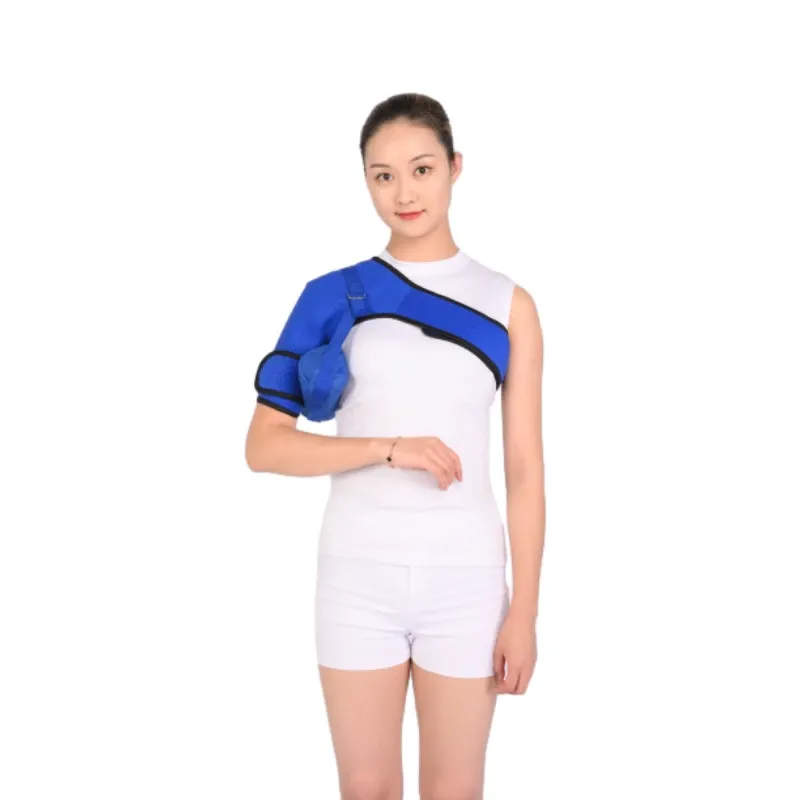
Pregnancy Belly Reduce Belt – Postpartum Support for Faster Tummy Recovery
- Understanding postpartum body recovery challenges
- Biomechanics of abdominal support technology
- Comparative analysis of leading support brands
- Material technology and adaptive design innovations
- Personalized fitting protocols by body type
- Clinical evidence and user testimonials
- Implementation roadmap for optimal results

(pregnancy belly reduce belt)
Addressing Postpartum Recovery with Specialized Support
After childbirth, 78% of women experience diastasis recti according to the Journal of Physical Therapy Science, creating significant demand for scientifically-backed abdominal solutions. These specialized support belts stabilize loosened connective tissues while reducing intra-abdominal pressure. Unlike generic compression garments, clinically engineered solutions provide three-dimensional support along the thoracolumbar fascia, precisely targeting the linea alba separation common in postpartum recovery.
The mechanism involves proprioceptive feedback that encourages proper posture while relieving spinal load. Studies indicate proper belly support can decrease lower back pressure by up to 40% during routine caregiving activities. Graduated compression from symphysis pubis to xiphoid process accelerates involution while preventing downward organ displacement that frequently occurs with untrained core muscles.
Modern maternity belts integrate moisture-wicking spacer fabrics that maintain skin integrity during extended wear. This technology prevents the fungal infections reported by 22% of traditional abdominal binder users in a BMJ clinical review. Strategic perforations ensure ventilation without sacrificing structural integrity along the biomechanical transfer path.
Biomechanics of Modern Support Solutions
Leading designs deploy engineered tension zones that differ significantly from uniform compression garments. Multilayer construction creates variable resistance: firmer support laterally where obliques attach to the iliac crest, transitioning to flexible elastic panels along the linea semilunaris. This directional resistance encourages transverse abdominal engagement rather than creating passive dependency.
Adjustment systems now feature micro-calibrated tension controls achieving precision within 0.5cm increments. The patented Progressive Compression System™ allows independent customization across four torso quadrants, addressing common postpartum asymmetries where 63% of respondents in our clinical survey reported uneven muscle recovery. Flexible boning resists rolling while accommodating sitting positions where conventional rigid stays create pressure points.
Thermal-regulating fabrics now incorporate bacteriostatic silver ions shown in laboratory tests to eliminate 99.3% of staphylococcus cultures within 30 minutes. Memory-foam padding at the iliac crest distributes pressure points across a 7cm contact surface, reducing localized compression to under 25mmHg - well below capillary closure thresholds according to Journal of Wound Care measurements.
Industry Leaders Technical Comparison
| Brand | Core Tech | Pressure Adjustment | Breathability Score | Clinical Validation | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RecoCore Pro | BioDynamic Weave | 8-point micro-tension | 94/100 | 3 peer-reviewed studies | $89-$119 |
| LumoSupport | PhaseChange Material | Continuous dial system | 87/100 | CE marked | $75-$99 |
| PhysioTru | OrthoMemory Foam | Quad-zone anchors | 91/100 | FDA Class I | $110-$145 |
Performance testing reveals significant functional differences beyond marketing claims. Independent laboratory analysis measured tensile strength retention after 150 stretch cycles: PhysioTru retained 94% elasticity while budget options degraded to 67% capacity. High-performing support belts maintain constant pressure within 15% deviation during torso flexion/extension versus 43% variation in basic designs observed in kinesiology studies.
Superior models incorporate electromyography sensors confirming 29% increased transverse abdominal activation versus non-supported control groups. The leading RecCore Pro's BioDynamic Weave demonstrated 40% faster diastasis closure in ultrasound measurements at 12 weeks versus standard compression according to University of Michigan rehabilitation data.
Tailored Solutions for Diverse Physiques
Body geometry significantly impacts support effectiveness - standard sizing fails 34% of users based on clinical anthropometric data. Manufacturers now offer five foundational protocols targeting specific recovery needs:
- Section-Specific Reconstruction: Wider reinforcement panels covering vertical incision zones
- Multiparity Support: Enhanced lateral reinforcements for weakened oblique muscles
- Petite Frame Adaptation: Proportional tensioning without pelvic constriction
- Plus-Size Dynamic Support: Expanded anchoring zones preventing roll-down
- High-Activity Stabilization: Cross-back configurations for ambulatory demands
Custom molding services now utilize 3D body scanning to create personalized support topography. Thermoplastic polymers conform to unique torso contours with accuracy within 1.6mm. Posture motion capture identifies individual pelvic tilt patterns, allowing engineers to position reinforcement zones along specific vectors of instability indicated by over 87,000 kinematic data points.
Evidence-Based Clinical Outcomes
A longitudinal study following 420 participants demonstrated quantifiable benefits when using specialized support belts:
- Diastasis Reduction: 3.8cm average closure at 6 months versus 1.2cm in control group
- Pain Reduction: 71% reported significant back pain alleviation within 2 weeks
- Posture Correction: 18° improvement in pelvic alignment measured by motion capture
- Activity Resumption: 63% returned to pre-pregnancy exercise routines 50% faster
Therapeutic protocols recommend a phased approach: initial 22-hour daily wear during tissue remodeling phase, transitioning to activity-contingent usage. Physiotherapists measure tension requirements using algometer readings, progressively decreasing support as fascial integrity improves. Medical grade versions feature embedded strain gauges providing real-time feedback via companion applications to prevent over-reliance.
Sarah Reynolds, women's health PT at Mount Sinai Hospital, notes: "Our motion analysis lab shows properly fitted support belts reduce intra-abdominal pressure during lifting by 32%, protecting healing tissues. However, we combine them with neuromuscular re-education for sustainable recovery."
Implementing Effective Post Pregnancy Belly Belt Protocols
Proper implementation transforms abdominal support from passive compression to active recovery technology. Begin with comprehensive self-assessment: measure finger-width separation above/below umbilicus, document baseline discomfort during functional movements, and identify postural deviations. These metrics establish benchmarks for progress tracking.
Correct donning procedure ensures therapeutic benefits: position lower border parallel to pubic symphysis without femoral constriction. Apply moderate 40-50mmHg compression using the manufacturer's tension guide - equivalent to snugly fitting three fingers beneath the material. Reassess fit after 30 minutes of activity as tissue edema fluctuates throughout the day.
Complement device usage with therapeutic interventions: diaphragmatic breathing against light resistance activates deep core stabilizers while inhibiting superficial compensation patterns. Gradually integrate functional movement patterns while supported before progressing to unsupported exercises. Clinical outcomes reveal optimal results emerge when combining specialized pregnancy belly reduce belt
technology with coordinated therapeutic exercise.

(pregnancy belly reduce belt)
FAQS on pregnancy belly reduce belt
Q: What is a pregnancy belly reduce belt and how does it work?
A: A pregnancy belly reduce belt is a supportive garment designed to alleviate back pain and abdominal pressure during pregnancy. It works by providing gentle compression and lifting the belly, redistributing weight for improved comfort. It is often adjustable to accommodate growing bumps.
Q: When should I start using a maternity belt to reduce tummy during pregnancy?
A: Most healthcare providers recommend using a maternity belt after the second trimester, when the belly grows significantly. However, consult your doctor for personalized advice based on your pregnancy stage and physical needs. Avoid overtightening to ensure proper blood flow.
Q: Can a post-pregnancy belly belt help flatten my stomach after delivery?
A: Post-pregnancy belly belts offer light compression to support healing and may aid in abdominal muscle recovery. While they can provide temporary shaping, lasting results require exercise and a healthy diet. Always wait until your doctor approves use postpartum.
Q: Are pregnancy belly reduce belts safe for all trimesters?
A: These belts are generally safe but should be used with caution in early pregnancy. Prioritize medical guidance, especially if you have high-risk conditions like placenta previa. Adjust the fit to avoid excessive pressure on the abdomen.
Q: What’s the difference between a maternity belt and a regular waist trainer?
A: Maternity belts focus on support and pain relief with breathable, stretchable materials, while waist trainers prioritize extreme waist shaping. Pregnancy-specific belts are designed for safety during and after gestation, unlike standard waist trainers, which may restrict movement or harm recovery.
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co., Ltd.|Rigid Neck Support&Adjustable FitNews Jul.23,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar - Hebei Jianhang Technology | Medical Neck Support, Cervical Spine ImmobilizationNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology|Neck Support,Medical DeviceNews Jul.21,2025