Feb . 12, 2025 16:28
Back to list
Hard Collar With Chin
Understanding the intricacies of arm slings is essential for those who are seeking optimal recovery following an injury or surgery. As supportive devices, arm slings play a crucial role in the healing process by immobilizing and protecting the arm, whether due to a fracture, sprain, rotator cuff surgery, or any other upper limb trauma. Delving into the nuances of arm slings offers valuable insights for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Caring for an arm sling is an aspect that should not be overlooked. Regular cleaning, especially for cotton slings, can prevent skin irritation and odors. Most slings are machine washable; however, it is advised to follow specific washing instructions provided by the manufacturer to maintain the sling's durability and effectiveness. Medical professionals often emphasize that an arm sling should complement, not replace, comprehensive rehabilitative care, including physiotherapy and prescribed exercises. This holistic approach encourages a swifter and more efficient recovery by combining mechanical support with therapeutic movement, ultimately reducing downtime and enhancing quality of life. The authoritative endorsement of arm slings by healthcare experts underscores their indispensability in post-injury recovery plans. Trust in these devices is cemented by years of empirical research and clinical trials, consistently validating their efficacy in aiding recovery from a diverse array of upper limb injuries. In the realm of patient experience, feedback indicates a high level of satisfaction with modern arm sling designs and materials, particularly those that offer both comfort and support without compromising mobility. These advancements reflect a growing trend towards more ergonomic and user-friendly medical aids, driven by a commitment to patient-centered care. In summary, arm slings are versatile recovery aids, tailored to meet the nuances of individual injuries with precision. By understanding their material composition, design intricacies, and appropriate usage, both patients and professionals can leverage these supports to foster effective and timely recovery. As such, their role as a fundamental component of injury management is both respected and well-established within the medical community.
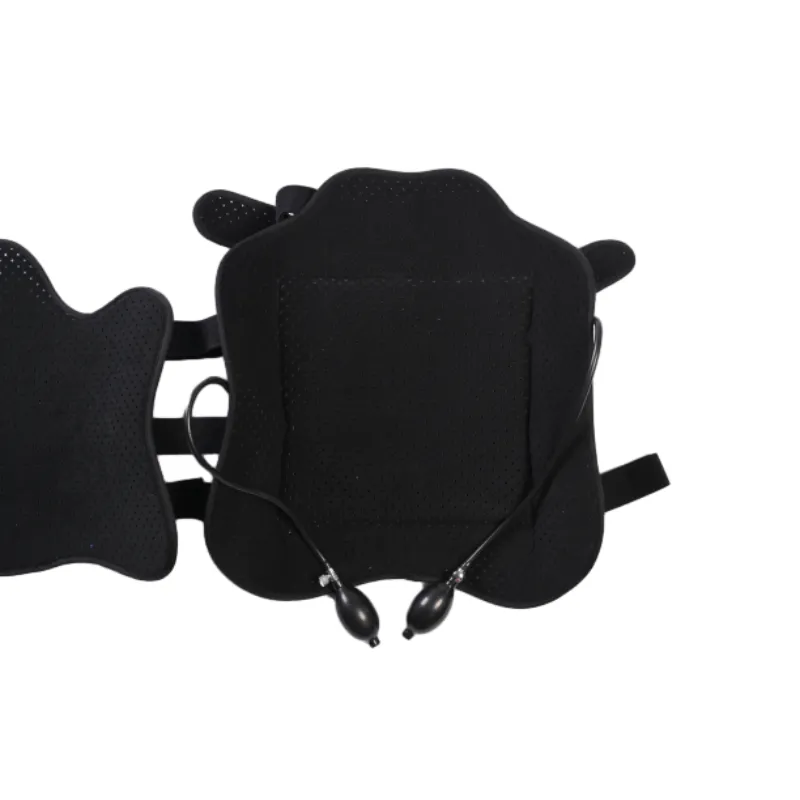
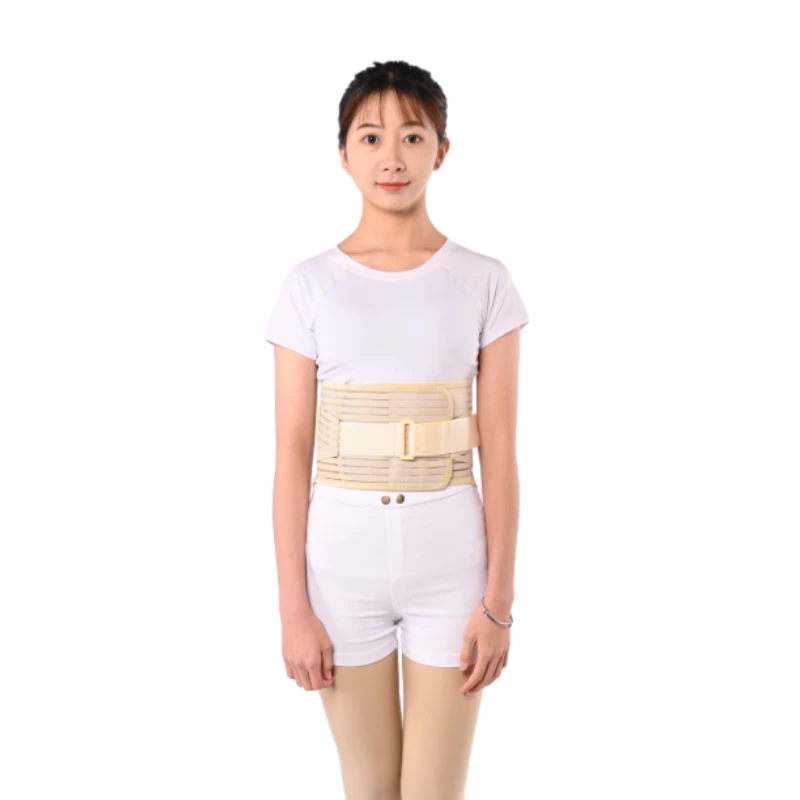


Caring for an arm sling is an aspect that should not be overlooked. Regular cleaning, especially for cotton slings, can prevent skin irritation and odors. Most slings are machine washable; however, it is advised to follow specific washing instructions provided by the manufacturer to maintain the sling's durability and effectiveness. Medical professionals often emphasize that an arm sling should complement, not replace, comprehensive rehabilitative care, including physiotherapy and prescribed exercises. This holistic approach encourages a swifter and more efficient recovery by combining mechanical support with therapeutic movement, ultimately reducing downtime and enhancing quality of life. The authoritative endorsement of arm slings by healthcare experts underscores their indispensability in post-injury recovery plans. Trust in these devices is cemented by years of empirical research and clinical trials, consistently validating their efficacy in aiding recovery from a diverse array of upper limb injuries. In the realm of patient experience, feedback indicates a high level of satisfaction with modern arm sling designs and materials, particularly those that offer both comfort and support without compromising mobility. These advancements reflect a growing trend towards more ergonomic and user-friendly medical aids, driven by a commitment to patient-centered care. In summary, arm slings are versatile recovery aids, tailored to meet the nuances of individual injuries with precision. By understanding their material composition, design intricacies, and appropriate usage, both patients and professionals can leverage these supports to foster effective and timely recovery. As such, their role as a fundamental component of injury management is both respected and well-established within the medical community.
Prev:
Next:
Latest News
-
Abduction Pillow Brace: Comfortable Hip Support Post-SurgeryNews Aug.01,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar - Hebei Jianhang Technology Co., Ltd.|Neck Support, Comfort, StabilityNews Aug.01,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar - Hebei Jianhang | Neck Support, Adjustable FitNews Aug.01,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar - Hebei Jianhang Technology Co., Ltd.|Advanced Neck Support, Adjustable FitNews Aug.01,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar - Hebei Jianhang Technology Co., Ltd.|Neck Support&Comfortable DesignNews Jul.31,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar - Hebei Jianhang Technology Co., Ltd.|Adjustable Neck Support, Lightweight Cervical CollarNews Jul.30,2025
Have a question? Keep in touch.