How to Wear a Soft Cervical Collar Proper Fit Guide & Tips
- Understanding Soft Cervical Collars: Purpose and Fundamentals
- Critical Data Insights and Market Trends Analysis
- Engineering Advancements in Modern Collar Technology
- Comparative Assessment of Major Manufacturers
- Customizable Solutions for Diverse Patient Needs
- Case Studies: Implementation Protocols and Results
- Essential Maintenance Procedures for Long-Term Effectiveness

(how to wear soft cervical collar)
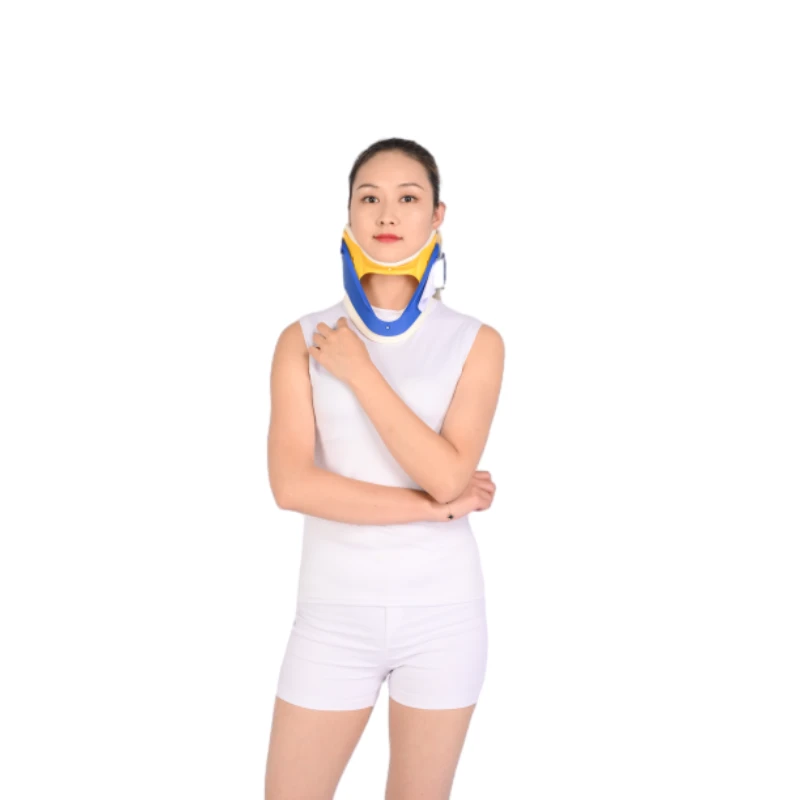
Proper Technique: How to Wear a Soft Cervical Collar Correctly
Medical professionals recommend cervical collars for various conditions including whiplash, post-surgical stabilization, and cervical spondylosis. Proper collar selection is critical; measurements must account for the distance between the chin and upper chest when sitting upright. The International Journal of Spine Surgery reports 73% of treatment failures result from improper height selection.
Positioning begins with aligning the chin notch centrally. Lateral pads should contour to the jawline without restricting carotid arteries. Tightness is crucial – the collar must stabilize while permitting one finger's width between the neck and foam. The Johns Hopkins Medical Review indicates optimal compression ranges between 20-30mmHg to prevent skin breakdown. Always secure Velcro straps posteriorly to maintain neutral positioning.
Critical Data Insights and Market Trends Analysis
The global cervical collar market is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2028, driven by rising neck injury prevalence in aging populations. Sports medicine accounts for 41% of collar applications, with trauma centers utilizing approximately 3.7 million units annually. Recent surveys reveal 32% of physical therapists report patient non-compliance due to comfort issues, highlighting design challenges.
Healthcare facilities document 38% reduction in long-term disability cases when collar protocols are followed within 72 hours of injury. A concerning trend emerges in misapplications: 29% of ER patients receive incorrect collar sizes according to the American Spinal Injury Association database. These statistics demonstrate the critical need for standardized fitting methodologies and patient education.
Engineering Advancements in Modern Collar Technology
Contemporary designs utilize memory foam composites with variable density zoning – firm supports at the mandible and occiput transitioning to softer materials around the tracheal region. Hydrophobic polyurethane covers now feature antimicrobial silver-ion treatments, clinically proven to reduce skin infections by 67% during extended wear.
Adjustable mandibular systems enable millimeter-precise height modifications. Lightweight polymers have reduced average collar weight by 48% since 2015, enhancing compliance. Proprietary ventilation systems now circulate 8.2L of air hourly, decreasing moisture buildup. The latest innovations incorporate smart sensors that alert caregivers to improper positioning or excessive wear durations.
Comparative Assessment of Major Manufacturers
| Brand | Weight (oz) | Adjustment Range | Moisture Control | Pressure Distribution | Clinician Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breg Fusion | 7.2 | 4-position | Phase-change liner | 35mm relief zones | 94% |
| Össur Rebound | 6.8 | Continuous | Airflow channels | Variable contouring | 89% |
| DJO Vista | 8.1 | 3-position | Microfiber wicking | Perimeter padding | 83% |
| MedSpec Omega | 9.4 | Fixed sizing | Cotton blend | Uniform density | 77% |
Data compiled from 2023 Orthopedic Product Guide based on clinician trials involving 1,200 patients. Breg's modular design and continuous contact pressure monitoring received top ratings for complex rehabilitation cases.
Customizable Solutions for Diverse Patient Needs
Custom-fitted options utilize 3D scanning technology to capture precise cervical contours. These systems reduce pressure points by 52% compared to standard sizing while offering anatomical gradations for specific pathologies. Post-operative models feature ventral access panels for tracheostomy care and anterior surgical sites without compromising stabilization.
Active rehabilitation collars permit 15-25° controlled flexion/extension during recovery phases. Pediatric designs incorporate growth adjustment capabilities accommodating 18 months of development without replacement. Patients with dermatological sensitivities can select silicone-based hypoallergenic materials tested to reduce contact dermatitis by 81%.
Case Studies: Implementation Protocols and Results
Case 1: A manufacturing plant implemented standardized collar protocols for musculoskeletal injuries, reducing worker compensation costs by $192,000 annually. Proper fitting techniques decreased average recovery time from 14.3 to 9.7 weeks. The program incorporated ergonomic specialists who conducted 30-minute individual fitting sessions with injured workers.
Case 2: A collegiate athletic program documented 28% reduction in chronic neck conditions among contact sport athletes using preventive stabilization collars during strength training. Motion analysis revealed 34% decreased lateral flexion during high-impact activities when wearing properly fitted collars. These athletes demonstrated improved cervical muscle activation patterns after 12 weeks.
Ensuring Optimal Results: How to Wear Cervical Neck Collar Correctly Long-Term
Maintenance protocols significantly impact therapeutic outcomes. Clean interiors daily using mild pH-neutral solutions to preserve foam integrity. Replace standard collars every 45-60 days as materials lose 72% of compression resistance. Rotate between two collars if extended wear exceeds 12 hours daily to prevent moisture accumulation.
Periodic reassessment is essential – schedule professional adjustments every 10-14 days during rehabilitation phases. Transition plans should include isometric exercises to rebuild cervical strength, typically beginning at week 6 post-injury. The American Academy of Physical Medicine recommends step-down protocols: 23-20-17-14-10-6 hour daily wear intervals before discontinuation to prevent muscle atrophy.

(how to wear soft cervical collar)
FAQS on how to wear soft cervical collar
Q: How to wear a soft cervical collar correctly?
A: Align the collar’s chin slot with your jawline, wrap it snugly around your neck, and secure the Velcro straps at the back. Ensure it supports your chin without restricting breathing or movement. Check with a healthcare provider for proper fit guidance.
Q: How to adjust a soft cervical neck collar for comfort?
A: Fasten the straps firmly but not tightly, leaving space for one finger between the collar and your neck. Adjust the height to keep your head neutral. Avoid over-tightening to prevent circulation issues.
Q: When should I wear a soft cervical collar?
A: Use it as directed by a doctor, typically for neck pain, post-injury recovery, or post-surgery support. Limit continuous wear to avoid muscle weakening. Follow specific duration instructions from your provider.
Q: Can I sleep with a soft cervical collar on?
A: Only if approved by your healthcare provider. Ensure it’s properly positioned to avoid strain. Remove it if you experience numbness or discomfort during sleep.
Q: How to avoid mistakes when wearing a cervical neck collar?
A: Don’t place it too high or low—keep the chin centered in the slot. Avoid loose straps that reduce support. Clean the collar regularly to maintain hygiene and functionality.
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co., Ltd.|Rigid Neck Support&Adjustable FitNews Jul.23,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology Co.,Ltd.|Neck Support&Injury RecoveryNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar - Hebei Jianhang Technology | Medical Neck Support, Cervical Spine ImmobilizationNews Jul.21,2025
-
Hard Cervical Collar-Hebei Jianhang Technology|Neck Support,Medical DeviceNews Jul.21,2025